해당 내용은 책 <컨테이너 인프라 환경 구축을 위한 쿠버네티스/도커>에 나오는 내용이며 이는 개인적으로 공부하기 위해서 게시하는 글임을 알립니다.
커피 중독자되는 중…
프로메테우스로 모니터링 데이터 수집과 통합하기
프로메테우스는 젠킨스처럼 헬름으로 쉽게 설치할 수 있다. 다만 젠킨스 설치 때와 마찬가지로 NFS 디렉터리(/nfs_shared/prometheus)를 만들고, 만든 NFS 디렉터리를 쿠버네티스 환경에서 사용할 수 있도록 PV와 PVC로 구성해야 한다. 접근 ID(사용자 ID, 그룹 ID)는 1000번으로 설정한다.
MetalLB 관련 실습 내용은 아래 링크를 통해 확인할 수 있다.
일단 책의 Chapter 5.2.2를 펼쳐서 사전 작업을 진행해 본다.
커스터마이즈로 MetalLB 한 번에 만들기
커스터마이즈 명령을 사용하기 위해서 ~/_Book_k8sInfra.ch5/5.2.2/kustomize-install.sh를 실행해 커스터마이즈 압축 파일을 내려받는다.
kustomize-install.sh
#!/usr/bin/env bash
curl -L \
https://github.com/kubernetes-sigs/kustomize/releases/download/kustomize%2Fv3.6.1/kustomize_v3.6.1_linux_amd64.tar.gz -o /tmp/kustomize.tar.gz
tar -xzf /tmp/kustomize.tar.gz -C /usr/local/bin
echo "kustomize install successfully"
한 줄 한 줄 의미를 알아 보자.
kustomize-install.sh
#!/usr/bin/env bash
#curl은 사용자 상호 작용 없이 작동하도록 설계된 서버로 데이터를 전송하기 위한 명령줄 유틸리티이다.
#curl을 사용하면 HTTP, HTTPS, SCP, SFTP 및 FTP 등 지원되는 프로토콜 중 하나를 사용하여 데이터를 다운로드하거나 업로드할 수 있다.
#curl의 -L 옵션은 서버에서 HTTP 301이나 HTTP 302 응답이 왔을 경우 redirection URL로 따라간다는 것이다.
#301은 301, Permanently Moved
#Permanently라는 뜻이 영구히, 영구적인 이라는 뜻이므로, 영구적으로 이동한다는 것이다. 요청된 리소스가 영구적으로 이동 페이지로 이동되었다는 것이다.
#302, Temporarily Moved
#Temporarily라는 뜻이 임시적, 임시적인 이라는 뜻이므로, 임시적으로 이동했다는 것을 나타냅니다. 요청된 리소스가 임시적으로 이동 페이지로 이동되었다는 것이다.
# '\' 표시는 줄바꿈하는 것이다.
curl -L \
#-o 옵션은 해당 링크에서 다운로드 받은 결과를 지정한 /tmp 아래 kustomize.tar.gz라는 이름의 파일로 저장한다.
#윈도우에서 기본적이고 많이 사용하는 압축 형식이 zip이라면
#리눅스에서는 tar.gz를 많이 사용한다. 리눅스에서 tar.gz는 별도의
#설치 없이 기본적으로 지원하는 압축 형식이다.
https://github.com/kubernetes-sigs/kustomize/releases/download/kustomize%2Fv3.6.1/kustomize_v3.6.1_linux_amd64.tar.gz -o /tmp/kustomize.tar.gz
#tar -xzf는 압축을 해제하는 명령이다.
#tar 옵션 -x: 묶음을 해제
#-z: gunzip을 사용
#-f: 파일 이름을 지정
#즉 /tmp 아래 kustomize.tar.gz 파일의 압축을 해제한다.
#-C 옵션은 압축을 해제한 다음에 /usr/local/bin 디렉터리에 넣으라는 것이다.
#이를 통해 배시 쉘에서 바로 실행할 수 있게 만든다.
tar -xzf /tmp/kustomize.tar.gz -C /usr/local/bin
echo "kustomize install successfully"
위의 명령을 실행한다. 그 다음 커스터마이즈에서 리소스 및 주소 할당 영역(Pool)을 구성할 때 사용할 파일들을 확인하기 위해서 ~/_Book_k8sInfra/ch5/5.2.2 디렉터리로 이동하고 metallb-l2config.yaml, metallb.yaml, namespace.yaml이 있는 것을 확인하고 각각을 살펴보자.
metallb-l2config.yaml
apiVersion: v1
kind: ConfigMap
metadata:
namespace: metallb-system
name: config
data:
config: |
address-pools:
- name: nginx-ip-range
protocol: layer2
addresses:
- 192.168.1.11-192.168.1.13
metallb-l2config.yaml
#apiVersion: API 버전을 명시한다
#이 오브젝트를 생성하기 위해 사용하고 있는 쿠버네티스 API 버전이 어떤 것인지
#명시한다.
apiVersion: v1
#어떤 종류의 오브젝트를 생성하고자 하는지 명시한다.
kind: ConfigMap
#이름 문자열, UID, 그리고 선택적인 네임스페이스를 포함하여
#오브젝트를 유일하게 구분지어 줄 데이터이다.
#서비스 이름(name)은 config이다.
metadata:
#ConfigMap이 위치하는 네임스페이스를
#metallb-system로 한다.
namespace: metallb-system
name: config
data:
config: |
#metallb의 세부 설정
#address-pools의 이름을 nginx-ip-range로 설정한다.
address-pools:
- name: nginx-ip-range
#metallb에서 제공하는 로드밸런서의 동작 방식이다. 즉 L2 방식이다.
protocol: layer2
#metallb에서 제공하는 로드밸러서의 External 주소이다.
#이 범위 안에서 External 주소를 부여한다.
addresses:
- 192.168.1.11-192.168.1.13
metallb.yaml 설명은 생략한다.
metallb.yaml
apiVersion: policy/v1beta1
kind: PodSecurityPolicy
metadata:
labels:
app: metallb
name: speaker
namespace: metallb-system
spec:
allowPrivilegeEscalation: false
allowedCapabilities:
- NET_ADMIN
- NET_RAW
- SYS_ADMIN
fsGroup:
rule: RunAsAny
hostNetwork: true
hostPorts:
- max: 7472
min: 7472
privileged: true
runAsUser:
rule: RunAsAny
seLinux:
rule: RunAsAny
supplementalGroups:
rule: RunAsAny
volumes:
- "*"
---
apiVersion: v1
kind: ServiceAccount
metadata:
labels:
app: metallb
name: controller
namespace: metallb-system
---
apiVersion: v1
kind: ServiceAccount
metadata:
labels:
app: metallb
name: speaker
namespace: metallb-system
---
apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1
kind: ClusterRole
metadata:
labels:
app: metallb
name: metallb-system:controller
rules:
- apiGroups:
- ""
resources:
- services
verbs:
- get
- list
- watch
- update
- apiGroups:
- ""
resources:
- services/status
verbs:
- update
- apiGroups:
- ""
resources:
- events
verbs:
- create
- patch
---
apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1
kind: ClusterRole
metadata:
labels:
app: metallb
name: metallb-system:speaker
rules:
- apiGroups:
- ""
resources:
- services
- endpoints
- nodes
verbs:
- get
- list
- watch
- apiGroups:
- ""
resources:
- events
verbs:
- create
- patch
- apiGroups:
- extensions
resourceNames:
- speaker
resources:
- podsecuritypolicies
verbs:
- use
---
apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1
kind: Role
metadata:
labels:
app: metallb
name: config-watcher
namespace: metallb-system
rules:
- apiGroups:
- ""
resources:
- configmaps
verbs:
- get
- list
- watch
---
apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1
kind: ClusterRoleBinding
metadata:
labels:
app: metallb
name: metallb-system:controller
roleRef:
apiGroup: rbac.authorization.k8s.io
kind: ClusterRole
name: metallb-system:controller
subjects:
- kind: ServiceAccount
name: controller
namespace: metallb-system
---
apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1
kind: ClusterRoleBinding
metadata:
labels:
app: metallb
name: metallb-system:speaker
roleRef:
apiGroup: rbac.authorization.k8s.io
kind: ClusterRole
name: metallb-system:speaker
subjects:
- kind: ServiceAccount
name: speaker
namespace: metallb-system
---
apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1
kind: RoleBinding
metadata:
labels:
app: metallb
name: config-watcher
namespace: metallb-system
roleRef:
apiGroup: rbac.authorization.k8s.io
kind: Role
name: config-watcher
subjects:
- kind: ServiceAccount
name: controller
- kind: ServiceAccount
name: speaker
---
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: DaemonSet
metadata:
labels:
app: metallb
component: speaker
name: speaker
namespace: metallb-system
spec:
selector:
matchLabels:
app: metallb
component: speaker
template:
metadata:
annotations:
prometheus.io/port: "7472"
prometheus.io/scrape: "true"
labels:
app: metallb
component: speaker
spec:
containers:
- args:
- --port=7472
- --config=config
env:
- name: METALLB_NODE_NAME
valueFrom:
fieldRef:
fieldPath: spec.nodeName
- name: METALLB_HOST
valueFrom:
fieldRef:
fieldPath: status.hostIP
image: metallb/speaker:v0.8.2
imagePullPolicy: IfNotPresent
name: speaker
ports:
- containerPort: 7472
name: monitoring
resources:
limits:
cpu: 100m
memory: 100Mi
securityContext:
allowPrivilegeEscalation: false
capabilities:
add:
- NET_ADMIN
- NET_RAW
- SYS_ADMIN
drop:
- ALL
readOnlyRootFilesystem: true
hostNetwork: true
nodeSelector:
beta.kubernetes.io/os: linux
serviceAccountName: speaker
terminationGracePeriodSeconds: 0
tolerations:
- effect: NoSchedule
key: node-role.kubernetes.io/master
---
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: Deployment
metadata:
labels:
app: metallb
component: controller
name: controller
namespace: metallb-system
spec:
revisionHistoryLimit: 3
selector:
matchLabels:
app: metallb
component: controller
template:
metadata:
annotations:
prometheus.io/port: "7472"
prometheus.io/scrape: "true"
labels:
app: metallb
component: controller
spec:
containers:
- args:
- --port=7472
- --config=config
image: metallb/controller:v0.8.2
imagePullPolicy: IfNotPresent
name: controller
ports:
- containerPort: 7472
name: monitoring
resources:
limits:
cpu: 100m
memory: 100Mi
securityContext:
allowPrivilegeEscalation: false
capabilities:
drop:
- all
readOnlyRootFilesystem: true
nodeSelector:
beta.kubernetes.io/os: linux
securityContext:
runAsNonRoot: true
runAsUser: 65534
serviceAccountName: controller
terminationGracePeriodSeconds: 0
namespace.yaml
apiVersion: v1
kind: Namespace
metadata:
name: metallb-system
labels:
app: metallb
namespace.yaml
#버젼 명시
apiVersion: v1
#오브젝트 종류 명시
kind: Namespace
#오브젝트 이름 metallb-system으로 지정
metadata:
name: metallb-system
#레이블 지정
labels:
app: metallb
이제 커스터마이즈로 변경될 작업을 정의하기 위해서 kustomize create –namespace=metallb-system –resources namespace.yaml, metallb.yaml, metallb-l2config.yaml 명령으로 kustomization.yaml을 생성한다. 이때 –namespace는 작업의 네임스페이스를 설정하며, –resources 명령은 커스터마이즈 명령을 이용해서 kustomization.yaml를 만들기 위한 소스 파일을 정의한다.
kustomize create --namespace=metallb-system --resources namespace.yaml, metallb.yaml, metallb-l2config.yaml
생성한 kustomization.yaml 파일을 보자.
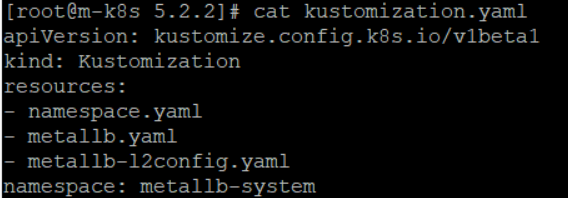
리소스로 namespace.yaml, metallb.yaml 그리고 metallb-l2config.yaml이 설정됐고, 네임스페이스는 metallb-system으로 설정된 것을 확인할 수 있다.
설치된 이미지를 안정적인 버전으로 유지하기 위해서 kustomize edit set image 옵션을 이용해 MetalLB controller와 speaker의 이미지 태그를 v0.8.2로 지정한다.
kustomize edit set image metallb/controller:v0.8.2
kustomize edit set image metallb/speaker:v0.8.2
커스터마이즈로 생성된 kustomization.yaml에 이미지 태그 정보(v0.8.2)가 설정됐는지 확인한다.
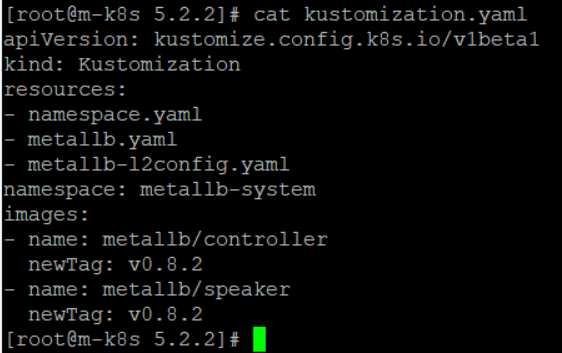
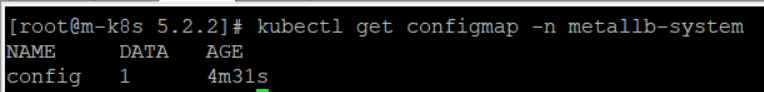
이제 kustomizae build 명령으로 MetalLB 설치를 위한 매니페스트를 생성해 보면, 다음과 같이 metallb-l2config.yaml을 통해서 컨피그맵이 만들어졌으며, 이미지 태그인 v0.8.2가 적용된 것을 확인할 수 있다.
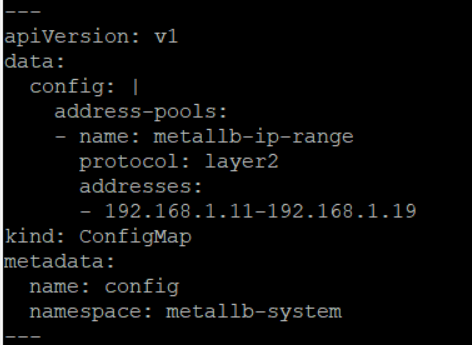
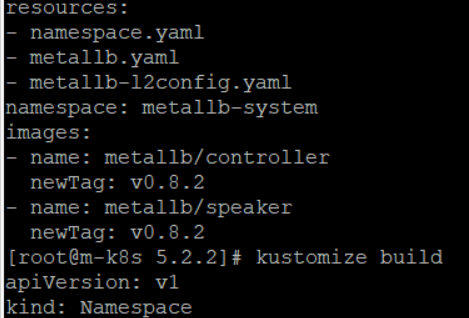
| 이를 파일로 저장해 MetalLB를 배포할 수도 있지만 편의를 위해서 **kustomize build | kubectl apply -f -** 명령으로 빌드한 결과한 바로 kubectl apply에 인자로 전달돼 배포되도록 한다. |
kustomize build | kubectl apply -f -
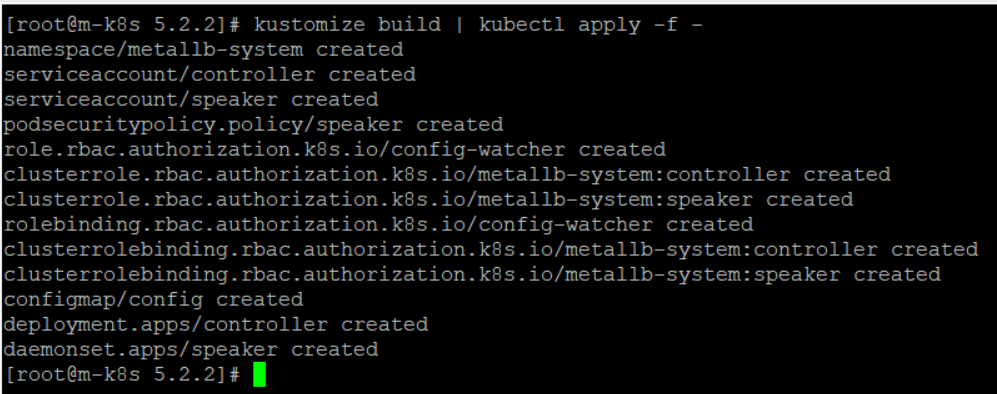
MetalLB가 정상적으로 배포됐는지 kubectl get pods -n metallb-system 명령과 kubectl get configmap -n metallb-system 명령으로 확인한다.
kubectl get pods -n metallb-system
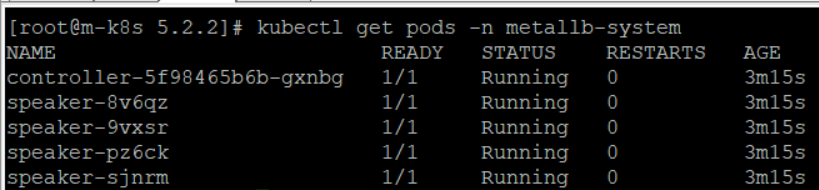
kubectl get configmap -n metallb-system
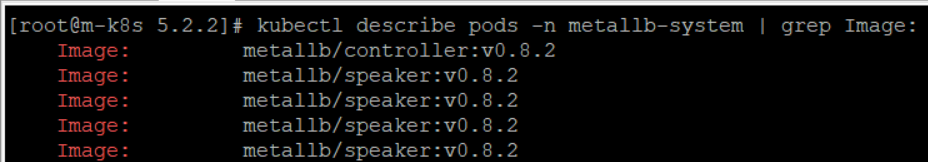
| **kubectl describe pods -n metallbe-system | grep Image:** 명령으로 커스터마이즈를 통해서 고정한 MetalLB의 태그가 v0.8.2인지 확인한다. |
kubectl describe pods -n metallb-system | grep Image:
kustomize build | kubectl delete -f -
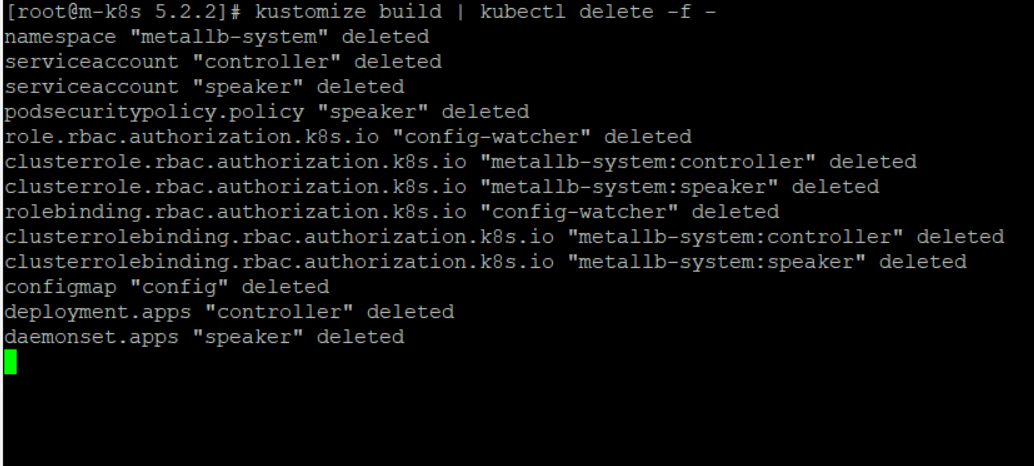
우리는 아래에서 헬름으로 MetalLB를 구성할 것이기 때문에 삭제를 한다.
헬름으로 배포 간편화하기
헬름을 통한 배포는 커스터마이즈에서 제한적이었던 주소 할당 영역과 같은 값을 대체하면서 간단하게 설치할 수 있도록 설계돼 있다. 헬름은 쿠버네티스에 패키지를 손쉽게 배포할 수 있도록 패키지를 관리하는 쿠버네티스 전용 패키지 매니저이다. 일반적으로 패키지는 실행 파일뿐만 아니라 실행 환경에 필요한 의존성 파일과 환경 정보들의 묶음이다.
커스터마이즈를 사용하면 많은 부분을 환경에 맞춰 변경할 수 있지만 주소 할당 영역과 같은 정보는 값의 형태가 아니라서 변경할 수가 없다. 이런 경우에 헬름을 사용하면 주소 할당 영역도 변경이 가능하다. 커스터마이즈에서 변경할 수 없는 값을 환경에 맞게 변경할 수 있다는 점 외에도 헬름은 여러 장점이 있다.
이제 헬름으로 MetalLB를 한 번에 만들어보자.
커스터마이즈를 통해서도 변동이 있는 값과 컨피그맵 파일을 쉽게 설치했었다. 헬름을 사용하면 얼마나 더 편해질까? 이제부터 확인해 보자.
헬름 명령을 사용하기 위해서 ~/_Book_k8sInfra/ch5/5.2.3/helm-install.sh를 실행해 헬름을 설치한다. helm-install.sh를 실행하면 항상 최신 버전의 헬름을 내려받기 때문에 호환성 이슈를 방지하기 위해서 DESIRED_VERSION 환경변수를 설정해 헬름 버전을 v3.2.1로 고정해 설치한다. 헬름 실행 파일도 /usr/local/bin에 위치시킨다.
export DESIRED_VERSION=v3.2.1; ~/Book_k8sInfra/ch5/5.2.3/helm-install.sh
helm-install.sh
#!/usr/bin/env bash
# Copyright The Helm Authors.
#
# Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License");
# you may not use this file except in compliance with the License.
# You may obtain a copy of the License at
#
# http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
#
# Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
# distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
# WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
# See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
# limitations under the License.
# The install script is based off of the MIT-licensed script from glide,
# the package manager for Go: https://github.com/Masterminds/glide.sh/blob/master/get
: ${BINARY_NAME:="helm"}
: ${USE_SUDO:="true"}
: ${DEBUG:="false"}
: ${VERIFY_CHECKSUM:="true"}
: ${VERIFY_SIGNATURES:="false"}
: ${HELM_INSTALL_DIR:="/usr/local/bin"}
HAS_CURL="$(type "curl" &> /dev/null && echo true || echo false)"
HAS_WGET="$(type "wget" &> /dev/null && echo true || echo false)"
HAS_OPENSSL="$(type "openssl" &> /dev/null && echo true || echo false)"
HAS_GPG="$(type "gpg" &> /dev/null && echo true || echo false)"
# initArch discovers the architecture for this system.
initArch() {
ARCH=$(uname -m)
case $ARCH in
armv5*) ARCH="armv5";;
armv6*) ARCH="armv6";;
armv7*) ARCH="arm";;
aarch64) ARCH="arm64";;
x86) ARCH="386";;
x86_64) ARCH="amd64";;
i686) ARCH="386";;
i386) ARCH="386";;
esac
}
# initOS discovers the operating system for this system.
initOS() {
OS=$(echo `uname`|tr '[:upper:]' '[:lower:]')
case "$OS" in
# Minimalist GNU for Windows
mingw*) OS='windows';;
esac
}
# runs the given command as root (detects if we are root already)
runAsRoot() {
local CMD="$*"
if [ $EUID -ne 0 -a $USE_SUDO = "true" ]; then
CMD="sudo $CMD"
fi
$CMD
}
# verifySupported checks that the os/arch combination is supported for
# binary builds, as well whether or not necessary tools are present.
verifySupported() {
local supported="darwin-amd64\nlinux-386\nlinux-amd64\nlinux-arm\nlinux-arm64\nlinux-ppc64le\nlinux-s390x\nwindows-amd64"
if ! echo "${supported}" | grep -q "${OS}-${ARCH}"; then
echo "No prebuilt binary for ${OS}-${ARCH}."
echo "To build from source, go to https://github.com/helm/helm"
exit 1
fi
if [ "${HAS_CURL}" != "true" ] && [ "${HAS_WGET}" != "true" ]; then
echo "Either curl or wget is required"
exit 1
fi
if [ "${VERIFY_CHECKSUM}" == "true" ] && [ "${HAS_OPENSSL}" != "true" ]; then
echo "In order to verify checksum, openssl must first be installed."
echo "Please install openssl or set VERIFY_CHECKSUM=false in your environment."
exit 1
fi
if [ "${VERIFY_SIGNATURES}" == "true" ]; then
if [ "${HAS_GPG}" != "true" ]; then
echo "In order to verify signatures, gpg must first be installed."
echo "Please install gpg or set VERIFY_SIGNATURES=false in your environment."
exit 1
fi
if [ "${OS}" != "linux" ]; then
echo "Signature verification is currently only supported on Linux."
echo "Please set VERIFY_SIGNATURES=false or verify the signatures manually."
exit 1
fi
fi
}
# checkDesiredVersion checks if the desired version is available.
checkDesiredVersion() {
if [ "x$DESIRED_VERSION" == "x" ]; then
# Get tag from release URL
local latest_release_url="https://github.com/helm/helm/releases"
if [ "${HAS_CURL}" == "true" ]; then
TAG=$(curl -Ls $latest_release_url | grep 'href="/helm/helm/releases/tag/v3.[0-9]*.[0-9]*\"' | grep -v no-underline | head -n 1 | cut -d '"' -f 2 | awk '{n=split($NF,a,"/");print a[n]}' | awk 'a !~ $0{print}; {a=$0}')
elif [ "${HAS_WGET}" == "true" ]; then
TAG=$(wget $latest_release_url -O - 2>&1 | grep 'href="/helm/helm/releases/tag/v3.[0-9]*.[0-9]*\"' | grep -v no-underline | head -n 1 | cut -d '"' -f 2 | awk '{n=split($NF,a,"/");print a[n]}' | awk 'a !~ $0{print}; {a=$0}')
fi
else
TAG=$DESIRED_VERSION
fi
}
# checkHelmInstalledVersion checks which version of helm is installed and
# if it needs to be changed.
checkHelmInstalledVersion() {
if [[ -f "${HELM_INSTALL_DIR}/${BINARY_NAME}" ]]; then
local version=$("${HELM_INSTALL_DIR}/${BINARY_NAME}" version --template="")
if [[ "$version" == "$TAG" ]]; then
echo "Helm ${version} is already ${DESIRED_VERSION:-latest}"
return 0
else
echo "Helm ${TAG} is available. Changing from version ${version}."
return 1
fi
else
return 1
fi
}
# downloadFile downloads the latest binary package and also the checksum
# for that binary.
downloadFile() {
HELM_DIST="helm-$TAG-$OS-$ARCH.tar.gz"
DOWNLOAD_URL="https://get.helm.sh/$HELM_DIST"
CHECKSUM_URL="$DOWNLOAD_URL.sha256"
HELM_TMP_ROOT="$(mktemp -dt helm-installer-XXXXXX)"
HELM_TMP_FILE="$HELM_TMP_ROOT/$HELM_DIST"
HELM_SUM_FILE="$HELM_TMP_ROOT/$HELM_DIST.sha256"
echo "Downloading $DOWNLOAD_URL"
if [ "${HAS_CURL}" == "true" ]; then
curl -SsL "$CHECKSUM_URL" -o "$HELM_SUM_FILE"
curl -SsL "$DOWNLOAD_URL" -o "$HELM_TMP_FILE"
elif [ "${HAS_WGET}" == "true" ]; then
wget -q -O "$HELM_SUM_FILE" "$CHECKSUM_URL"
wget -q -O "$HELM_TMP_FILE" "$DOWNLOAD_URL"
fi
}
# verifyFile verifies the SHA256 checksum of the binary package
# and the GPG signatures for both the package and checksum file
# (depending on settings in environment).
verifyFile() {
if [ "${VERIFY_CHECKSUM}" == "true" ]; then
verifyChecksum
fi
if [ "${VERIFY_SIGNATURES}" == "true" ]; then
verifySignatures
fi
}
# installFile installs the Helm binary.
installFile() {
HELM_TMP="$HELM_TMP_ROOT/$BINARY_NAME"
mkdir -p "$HELM_TMP"
tar xf "$HELM_TMP_FILE" -C "$HELM_TMP"
HELM_TMP_BIN="$HELM_TMP/$OS-$ARCH/helm"
echo "Preparing to install $BINARY_NAME into ${HELM_INSTALL_DIR}"
runAsRoot cp "$HELM_TMP_BIN" "$HELM_INSTALL_DIR/$BINARY_NAME"
echo "$BINARY_NAME installed into $HELM_INSTALL_DIR/$BINARY_NAME"
}
# verifyChecksum verifies the SHA256 checksum of the binary package.
verifyChecksum() {
printf "Verifying checksum... "
local sum=$(openssl sha1 -sha256 ${HELM_TMP_FILE} | awk '{print $2}')
local expected_sum=$(cat ${HELM_SUM_FILE})
if [ "$sum" != "$expected_sum" ]; then
echo "SHA sum of ${HELM_TMP_FILE} does not match. Aborting."
exit 1
fi
echo "Done."
}
# verifySignatures obtains the latest KEYS file from GitHub master branch
# as well as the signature .asc files from the specific GitHub release,
# then verifies that the release artifacts were signed by a maintainer's key.
verifySignatures() {
printf "Verifying signatures... "
local keys_filename="KEYS"
local github_keys_url="https://raw.githubusercontent.com/helm/helm/master/${keys_filename}"
if [ "${HAS_CURL}" == "true" ]; then
curl -SsL "${github_keys_url}" -o "${HELM_TMP_ROOT}/${keys_filename}"
elif [ "${HAS_WGET}" == "true" ]; then
wget -q -O "${HELM_TMP_ROOT}/${keys_filename}" "${github_keys_url}"
fi
local gpg_keyring="${HELM_TMP_ROOT}/keyring.gpg"
local gpg_homedir="${HELM_TMP_ROOT}/gnupg"
mkdir -p -m 0700 "${gpg_homedir}"
local gpg_stderr_device="/dev/null"
if [ "${DEBUG}" == "true" ]; then
gpg_stderr_device="/dev/stderr"
fi
gpg --batch --quiet --homedir="${gpg_homedir}" --import "${HELM_TMP_ROOT}/${keys_filename}" 2> "${gpg_stderr_device}"
gpg --batch --no-default-keyring --keyring "${gpg_homedir}/pubring.kbx" --export > "${gpg_keyring}"
local github_release_url="https://github.com/helm/helm/releases/download/${TAG}"
if [ "${HAS_CURL}" == "true" ]; then
curl -SsL "${github_release_url}/helm-${TAG}-${OS}-${ARCH}.tar.gz.sha256.asc" -o "${HELM_TMP_ROOT}/helm-${TAG}-${OS}-${ARCH}.tar.gz.sha256.asc"
curl -SsL "${github_release_url}/helm-${TAG}-${OS}-${ARCH}.tar.gz.asc" -o "${HELM_TMP_ROOT}/helm-${TAG}-${OS}-${ARCH}.tar.gz.asc"
elif [ "${HAS_WGET}" == "true" ]; then
wget -q -O "${HELM_TMP_ROOT}/helm-${TAG}-${OS}-${ARCH}.tar.gz.sha256.asc" "${github_release_url}/helm-${TAG}-${OS}-${ARCH}.tar.gz.sha256.asc"
wget -q -O "${HELM_TMP_ROOT}/helm-${TAG}-${OS}-${ARCH}.tar.gz.asc" "${github_release_url}/helm-${TAG}-${OS}-${ARCH}.tar.gz.asc"
fi
local error_text="If you think this might be a potential security issue,"
error_text="${error_text}\nplease see here: https://github.com/helm/community/blob/master/SECURITY.md"
local num_goodlines_sha=$(gpg --verify --keyring="${gpg_keyring}" --status-fd=1 "${HELM_TMP_ROOT}/helm-${TAG}-${OS}-${ARCH}.tar.gz.sha256.asc" 2> "${gpg_stderr_device}" | grep -c -E '^\[GNUPG:\] (GOODSIG|VALIDSIG)')
if [[ ${num_goodlines_sha} -lt 2 ]]; then
echo "Unable to verify the signature of helm-${TAG}-${OS}-${ARCH}.tar.gz.sha256!"
echo -e "${error_text}"
exit 1
fi
local num_goodlines_tar=$(gpg --verify --keyring="${gpg_keyring}" --status-fd=1 "${HELM_TMP_ROOT}/helm-${TAG}-${OS}-${ARCH}.tar.gz.asc" 2> "${gpg_stderr_device}" | grep -c -E '^\[GNUPG:\] (GOODSIG|VALIDSIG)')
if [[ ${num_goodlines_tar} -lt 2 ]]; then
echo "Unable to verify the signature of helm-${TAG}-${OS}-${ARCH}.tar.gz!"
echo -e "${error_text}"
exit 1
fi
echo "Done."
}
# fail_trap is executed if an error occurs.
fail_trap() {
result=$?
if [ "$result" != "0" ]; then
if [[ -n "$INPUT_ARGUMENTS" ]]; then
echo "Failed to install $BINARY_NAME with the arguments provided: $INPUT_ARGUMENTS"
help
else
echo "Failed to install $BINARY_NAME"
fi
echo -e "\tFor support, go to https://github.com/helm/helm."
fi
cleanup
exit $result
}
# testVersion tests the installed client to make sure it is working.
testVersion() {
set +e
HELM="$(command -v $BINARY_NAME)"
if [ "$?" = "1" ]; then
echo "$BINARY_NAME not found. Is $HELM_INSTALL_DIR on your "'$PATH?'
exit 1
fi
set -e
}
# help provides possible cli installation arguments
help () {
echo "Accepted cli arguments are:"
echo -e "\t[--help|-h ] ->> prints this help"
echo -e "\t[--version|-v <desired_version>] . When not defined it fetches the latest release from GitHub"
echo -e "\te.g. --version v3.0.0 or -v canary"
echo -e "\t[--no-sudo] ->> install without sudo"
}
# cleanup temporary files to avoid https://github.com/helm/helm/issues/2977
cleanup() {
if [[ -d "${HELM_TMP_ROOT:-}" ]]; then
rm -rf "$HELM_TMP_ROOT"
fi
}
# Execution
#Stop execution on any error
trap "fail_trap" EXIT
set -e
# Set debug if desired
if [ "${DEBUG}" == "true" ]; then
set -x
fi
# Parsing input arguments (if any)
export INPUT_ARGUMENTS="${@}"
set -u
while [[ $# -gt 0 ]]; do
case $1 in
'--version'|-v)
shift
if [[ $# -ne 0 ]]; then
export DESIRED_VERSION="${1}"
else
echo -e "Please provide the desired version. e.g. --version v3.0.0 or -v canary"
exit 0
fi
;;
'--no-sudo')
USE_SUDO="false"
;;
'--help'|-h)
help
exit 0
;;
*) exit 1
;;
esac
shift
done
set +u
initArch
initOS
verifySupported
checkDesiredVersion
if ! checkHelmInstalledVersion; then
downloadFile
verifyFile
installFile
fi
testVersion
cleanup
MetalLB을 설치하려면 헬름 차트를 등록할 주소를 알아야 한다. 아티팩트허브(https://artifacthub.io)에서 metallb를 검색해 주소를 확인한다.
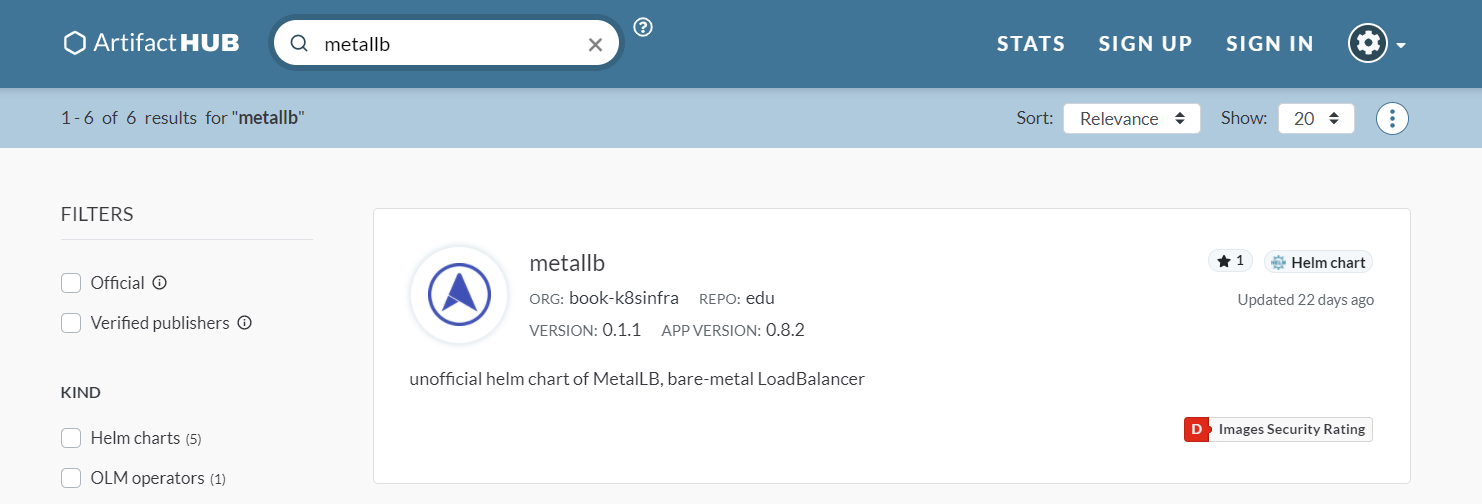
상단에 위치한 아이템을 눌러 metallb 차트에 대한 정보를 확인해 본다. metallb 아이템을 클릭하면 차트에 대한 상세한 내용을 확인할 수 있다.
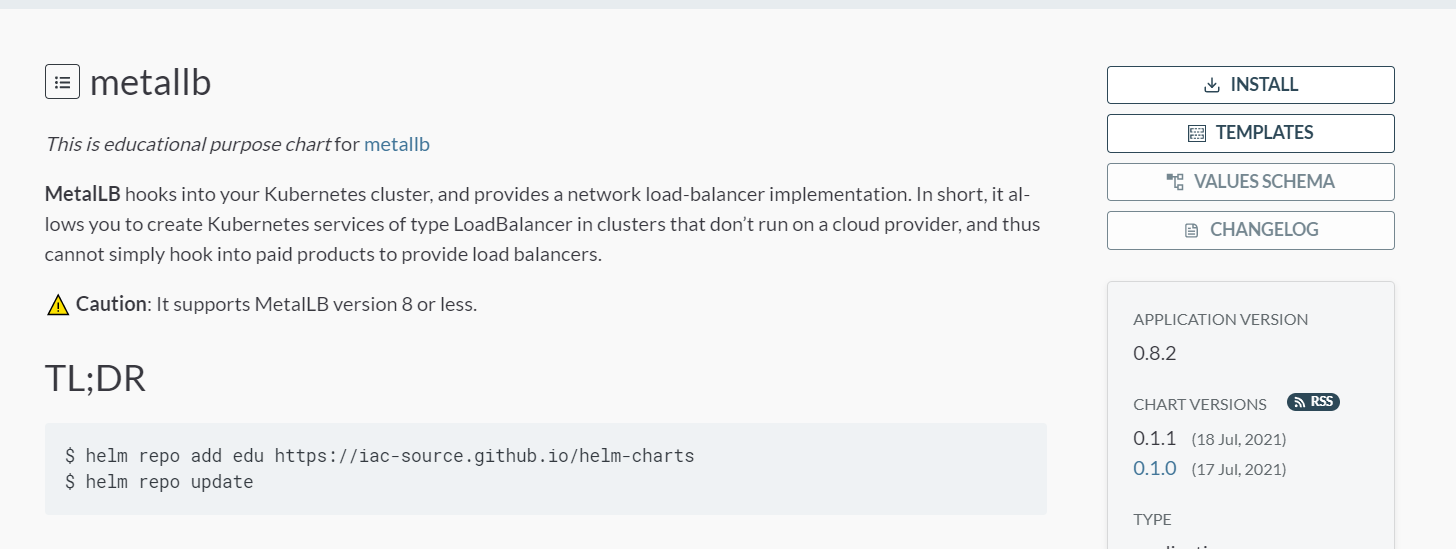
이제 헬름 차트 저장소의 주소도 확인했으니 실제로 저장소를 helm repo add 명령으로 등록해서 MetalLB를 설치할 준비를 한다. 여기서 혼동이 올 수 있는 부분이 있다. 헬름 차트 저장소인 https:iac-source.github.io/helm-chars는 책 저자가 만든 저장소로, 아티팩트허브에는 이 경로만을 표시한다는 점을 다시 한 번 기억한다. 그리고 edu는 헬름 차트 저장소를 대표하는 이름의 역할을 하는 것으로 자유롭게 변경 등록이 가능하지만, 책에서는 edu를 기반으로 작성됐기 때문에 이 책에서는 edu를 사용한다.
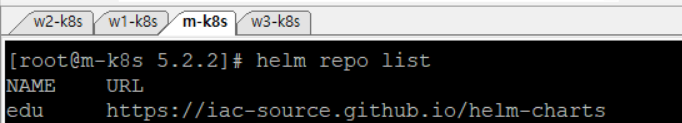
helm repo add edu https://iac-source.github.io/helm-charts

헬름 차트 저장소가 정상적으로 등록됐는지 helm repo list 명령으로 저장소 목록을 확인한다. 확인한 결과 edu라는 이름의 차트 저장소가 등록된 것을 확인할 수 있다.
헬름으로 차트 저장소를 추가한 시점의 차트를 로컬 캐시에 저장해 install과 같은 작업 수행시에 먼저 로컬에 있는 캐시 차트 정보를 참조한다. 만약 저장소 추가 이후에 변경된 차트가 있다면 변경된 정보를 캐시에 업데이트할 수 있도록 helm repo update 명령을 통해 최신 차트 정보를 동기화 한다. 이는 관습적으로 이루어지는 것으로 현재의 랩에서는 필요한 요소는 아니지만 진행하는 것이 나중에 일어날 수 있는 문제를 방지할 수 있다.
helm repo update
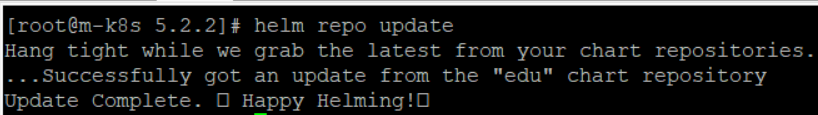
앞서 등록 및 업데이트한 저장소 edu로부터 MetalLB를 설치해본다. 헬름 차트를 설치할 때 사용하는 명령어 helm install이며 커스터마이즈와 다르게 인자를 바로 명령줄에서 받아서 처리한다. 현재 사용하는 인자는 다음과 같다.
-
–namespace: 헬름 차트를 통해서 생성되는 애플리케이션이 위치할 네임스페이스를 지정한다.
-
–create-namespace: 네임스페이스 옵션으로 지정된 네임스페이스가 존재하지 않는 경우 네임스페이스를 생성한다.
-
–set: 헬름에서 사용할 변수를 명령 인자로 전달한다. key1=value1, key2=value2와 같이 ,(쉽표)를 사용해 한 줄에서 여러 인자를 넘겨 줄 수 있으나 가독성을 높이기 위해 책에서는 ,로 여러 인자를 넘겨 사용하지 않는다.
일반적으로 배포 이후에 간략한 메시지와 함께 제작자가 작성한 사용 설명서가 함께 출력된다. 이제 사전에 구성된 스크립트를 통해 차트를 설치해본다.
helm install metallb edu/metallb \
--namespace=metallb-system \
--create-namespace \
--set controller.tag=v0.8.3 \
--set speaker.tag=v0.8.3 \
--set configmap.ipRange=192.168.1.11-192.168.1.29
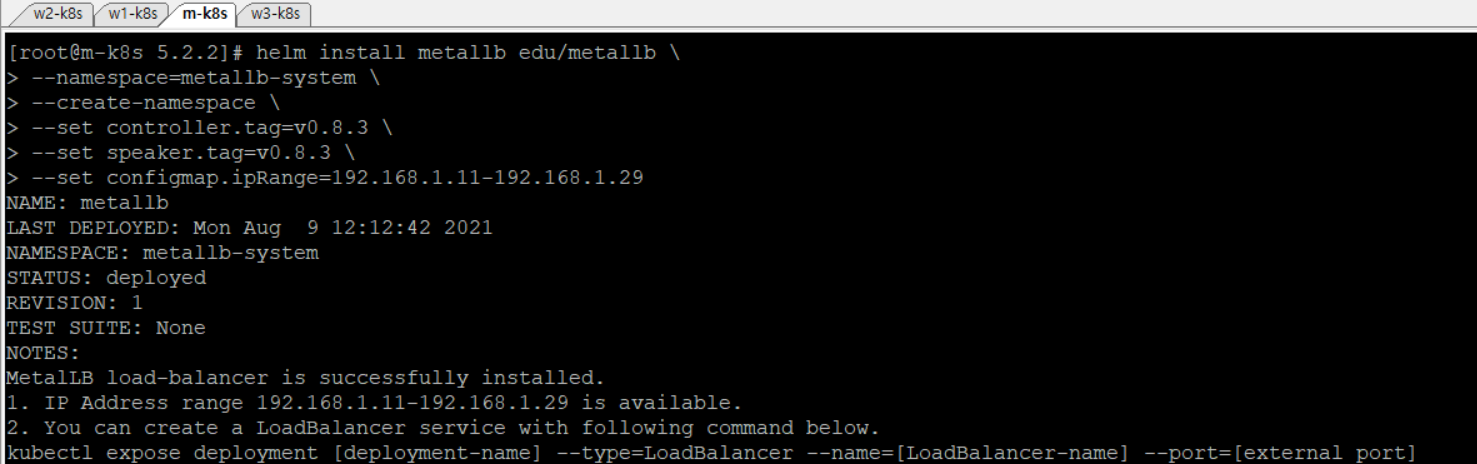
설치된 MetalLB가 정상적인 상태인지 배포 상태를 확인한다.
kubectl get pods -n metallb-system
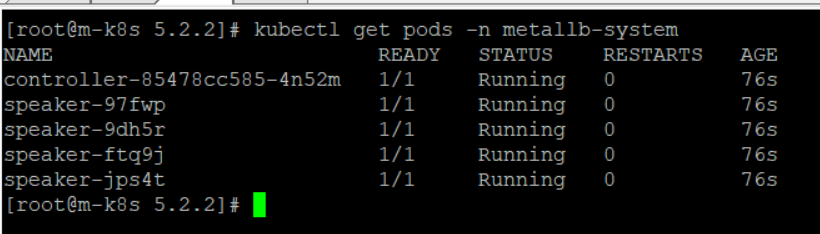
| **kubectl describe pods -n metallb-system | grep Image:** 명령으로 헬름 set 옵션을 통해서 변경된 MetalLB의 태그가 v0.8.3인지 확인한다. |
kubectl describe pods -n metallb-system | grep Image:
이제 사전 작업이 끝났으니 다음 게시물에서 프로메테우스를 설치해 보겠다.
